Hearing Loss Overview
Hearing loss is the third most common medical condition older adults experience today after heart disease and arthritis. Over 48 million people are impacted by hearing loss which exceeds rates of diabetes and even cancer. Hearing loss reduces an individual's capacity to hear and process speech as well as sound which takes a toll on communication - an essential way we navigate everyday life. Though nearly 1 in 6 people has some degree of hearing loss, it remains widely undertreated. Only a third of people who could benefit from treatment receive it. Treating hearing loss offers countless benefits including strengthening communication, relationships, and social life, and supporting overall health in ways that allow people to live active lives.
Causes
Hearing loss impacts people of all ages and various factors contribute to its development. This includes:
Other causes include inner ear disorders and chronic ear infections. These factors typically produce hearing loss over time meaning that impaired hearing occurs gradually.
Symptoms
Hearing loss produces a range of symptoms that can take time to become aware of. Common symptoms include the following:
- Tinnitus: a ringing or buzzing-like noise in one or both ears.
- Sounds are distorted or slurred, others sound like they are mumbling.
- Asking others to repeat what they said or to speak louder.
- Experiencing a tough time hearing in environments with background noise and in conversations with multiple people.
- Turning up the volume on the TV or other electronic devices.
- Lip reading to help identify individual words.
- Pretending to hear to get through a conversion.
- Feeling left out of conversations and social activities.
- Being exhausted after conversations with others.
These symptoms can be mild to severe depending on the degree of hearing loss present. Symptoms make it difficult to participate in conversations so this can lead to people avoiding them altogether. Social withdrawal is a major outcome of untreated hearing loss. This includes spending less time with others and skipping out on social activities as well as gatherings. These symptoms increase the risk of experiencing depressive symptoms and also increase other health risks. Untreated hearing loss increases the risk of cognitive decline, falls, and accidental injuries.
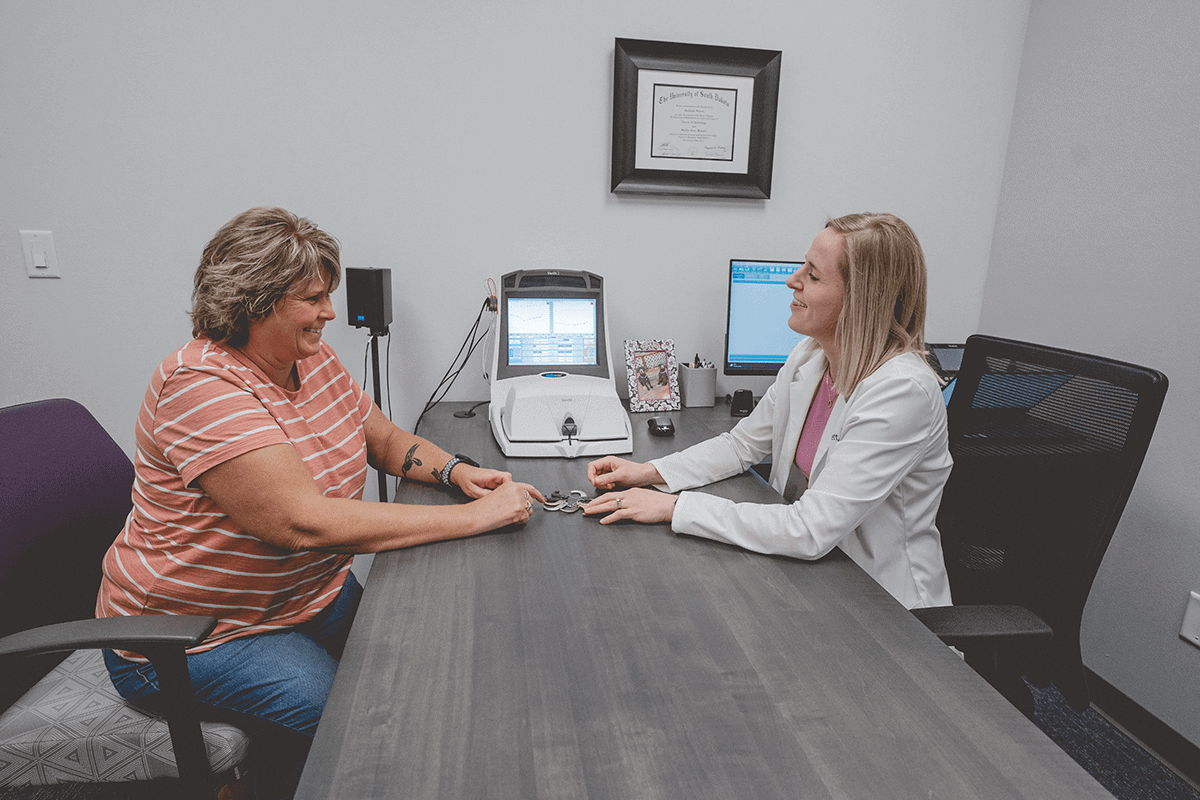

Diagnosis & Treatment
Hearing loss is diagnosed by a hearing healthcare specialist like an audiologist. The first step is to have your hearing health comprehensively assessed. Different hearing tests are used to measure hearing capacities in both ears. This involves a painless process that identifies any hearing loss and the degree of impairment in each ear. Once your hearing needs are established, treatment is tailored to meet those needs.
Hearing aids are the most common treatment for hearing loss. These hearing instruments are equipped with technology that absorbs, amplifies and processes sound. This alleviates symptoms and increases the capacity to hear. Hearing aids provide the ears and brain with significant support, making it easier to hear and engage in communication. Hearing aids strengthen communication, improve relationships, enrich social engagement, and boost overall health. These benefits enhance the quality of life and support people in fully participating in everyday life.
